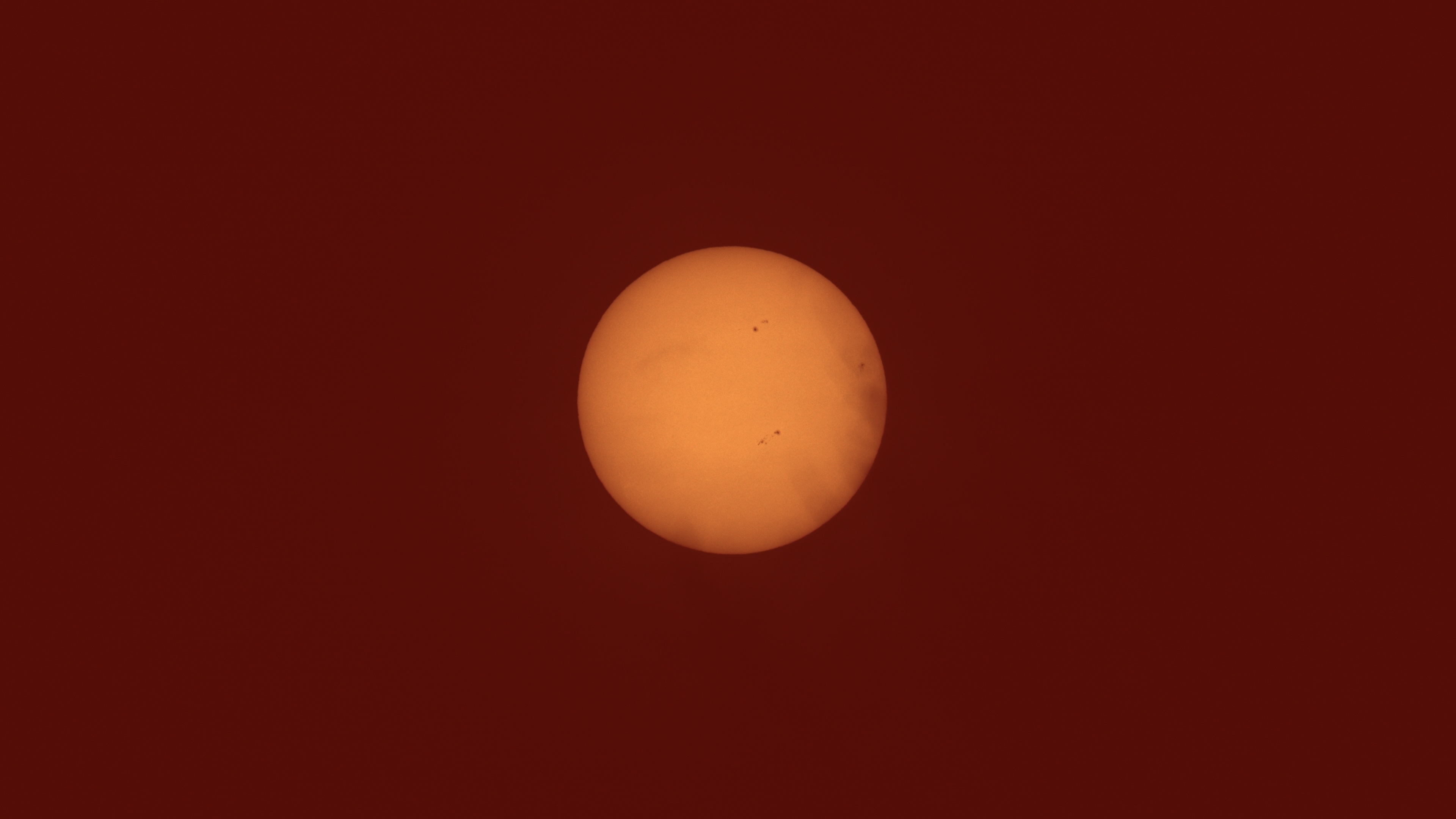
Overview of Sunspot AR3917
Sunspot AR3917 was a significant feature on the Sun's surface during mid-December 2024. It was the lead flare producer during this period, generating six C-class solar flares. These flares are categorized as relatively moderate in intensity but still capable of causing minor disturbances in Earth's upper atmosphere.
Magnetic Configuration
- Sunspot AR3917 exhibited a beta magnetic configuration, which is a simpler arrangement of magnetic fields compared to more complex configurations like beta-gamma or delta.
- This configuration indicates moderate potential for solar flaring activity, which aligns with the observed C-class flares.
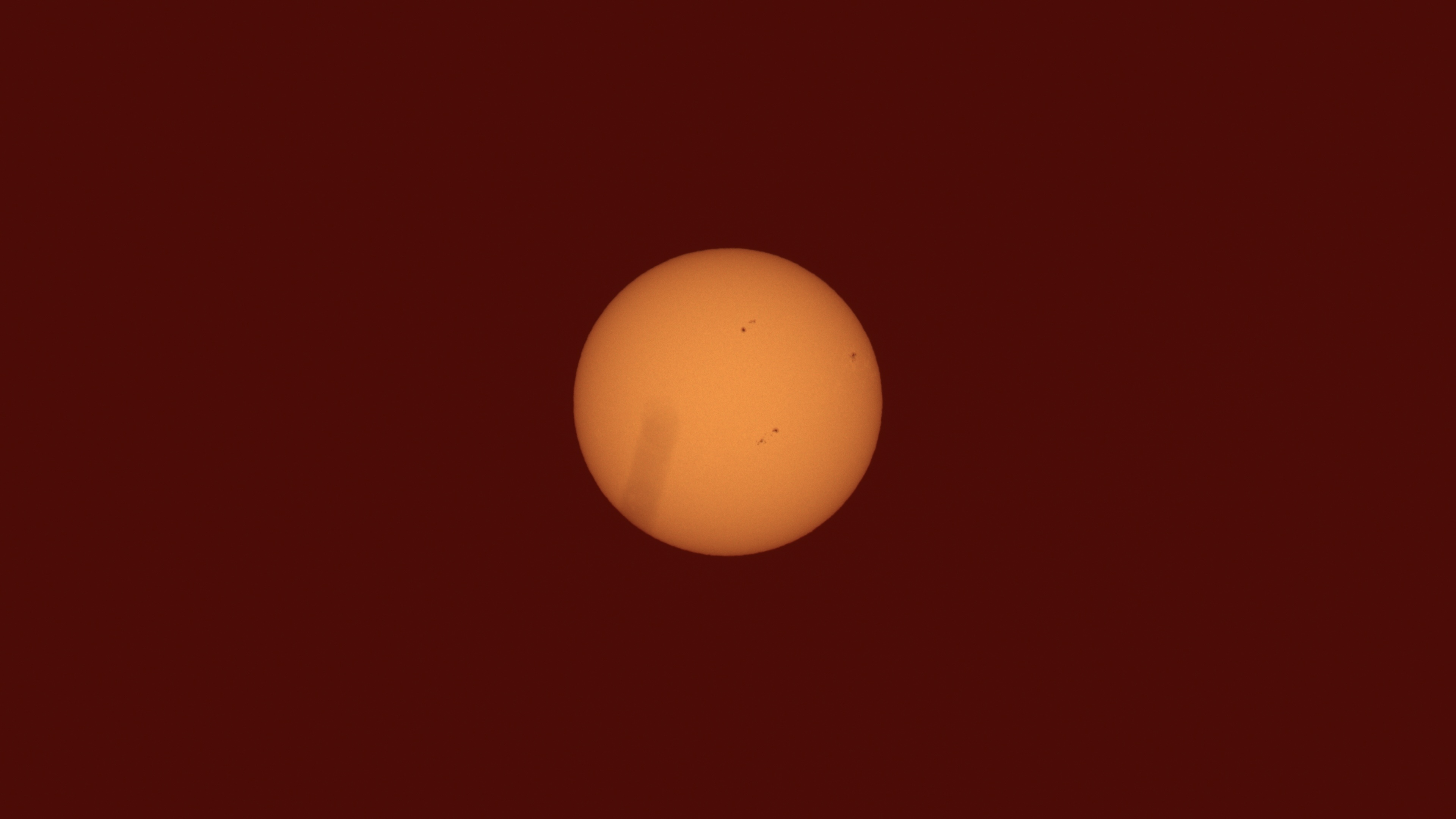
Solar Activity Context
- On December 14, 2024, the Sun had five active sunspot regions visible on its Earth-facing side.
- While AR3917 was the most active, other regions, such as AR3924, retained moderate flaring potential with a more complex beta-gamma magnetic configuration.
Significance of AR3917
Sunspot AR3917's activity contributed to the ongoing solar activity during Solar Cycle 25, which has been marked by increasing solar activity as it approaches its peak. The flares from AR3917, while not extreme, are part of the dynamic processes that influence space weather and can have minor effects on satellite communications and navigation systems.
Fun Fact
Sunspots like AR3917 are temporary dark regions on the Sun's surface caused by intense magnetic activity. These regions are cooler than their surroundings and are often associated with solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs), which can impact Earth's space environment.